
0. 引言:
最近写了一些异步递归的代码,着实有点头疼,索性重新研究一下JavaScript 代码执行顺序,并附上一道面试题的解析。
1. JavaScript 代码执行顺序
首先我们了解几个概念
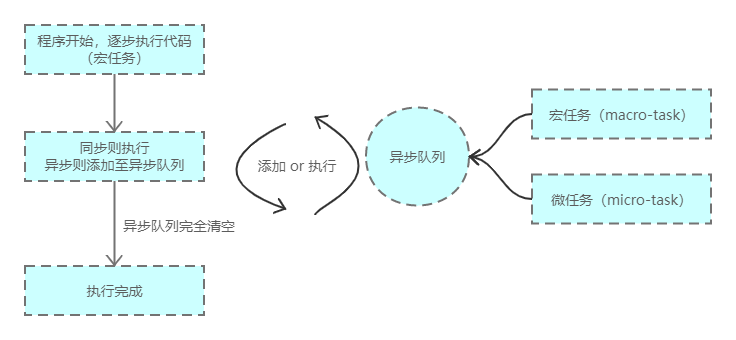
1.1 微任务/宏任务
异步队列中包括:微任务(micro-task) 和 宏任务(macro-task)
微任务包括: process.nextTick ,Promise ( process.nextTick 为 Node 独有)
宏任务包括: script , setTimeout ,setInterval ,setImmediate ,I/O ,UI rendering
Tips:
- 微任务优先级高于宏任务的前提是:同步代码已经执行完成。因为
script 属于宏任务,程序开始后会首先执行同步脚本,也就是script 。
Promise 里边的代码属于同步代码,.then() 中执行的代码才属于异步代码。
1.2 Event Loop(事件轮询)
Event Loop 是一个程序结构,用于等待和发送消息和事件。
Event Loop 执行顺序如下所示:
- 首先执行同步代码(宏任务)
- 当执行完所有同步代码后,执行栈为空,查询是否有异步代码需要执行
- 执行所有微任务
- 当执行完所有微任务后,如有必要会渲染页面
- 然后开始下一轮 Event Loop,执行宏任务中的异步代码,也就是
setTimeout 中的回调函数
Tips:简化讲:先执行一个宏任务(script同步代码),然后执行并清空微任务,再执行一个宏任务,然后执行并清空微任务,再执行一个宏任务,再然后执行并清空微任务……如此循环往复(一个宏任务 -> 清空微任务 -> 一个宏任务 -> 清空微任务)
2. 面试题详解
2.1 题目
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| setTimeout(function () {
console.log(" set1");
new Promise(function (resolve) {
resolve();
}).then(function () {
new Promise(function (resolve) {
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("then4");
});
console.log("then2 ");
});
});
new Promise(function (resolve) {
console.log("pr1");
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("then1");
});
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("set2");
});
console.log(2);
new Promise(function (resolve) {
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("then3");
});
|
2.2 执行过程解析
执行所有同步代码(第一次宏任务):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| setTimeout(function () {
console.log(" set1");
new Promise(function (resolve) {
resolve();
}).then(function () {
new Promise(function (resolve) {
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("then4");
});
console.log("then2 ");
});
});
new Promise(function (resolve) {
console.log("pr1");
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("then1");
});
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("set2");
});
console.log(2);
new Promise(function (resolve) {
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("then3");
});
|
执行并清空微任务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| function () {
console.log("then1");
}
function () {
console.log("then3");
}
|
执行一个宏任务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| function () {
console.log(" set1");
new Promise(function (resolve) {
resolve();
}).then(function () {
new Promise(function (resolve) {
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("then4");
});
console.log("then2 ");
});
}
|
执行并清空微任务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| function () {
new Promise(function (resolve) {
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("then4");
});
console.log("then2 ");
}
|
此时微任务列表增加并未清空,继续执行微任务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| function () {
console.log("then4");
}
|
执行宏任务
1
2
3
4
5
6
| function () {
console.log("set2");
}
|
完整输入顺序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| pr1
2
then1
then3
set1
then2
then4
set2
|
推荐阅读
如果您喜欢我的文章,希望能够关注我的微信公众号 RainCode,您的关注是莫大的鼓励 ❤




